Solid-state drives (SSDs) have faster performance and reliability compared to the traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). When it comes to SSDs, you may have come across terms like M.2, SATA, PCIe, and NVMe. So it is bit confusing to choose which SSD is support your motherboard.

In this article, we will explain what are M.2, SATA, PCIe, and NVMe SSDs, and how to determine if an M.2 SSD is compatible with your motherboard.
Table of Contents
What are M.2 SSDs (SATA, PCI, NVMe)?
M.2 is a form factor for SSDs that is becoming widely adopted in modern computers and laptops. M.2 SSDs are smaller and more compact than traditional 2.5-inch SSDs (SATA SSDs), making them ideal for devices with limited space. They connect directly to the motherboard using the M.2 slot, eliminating the need for cables.
M.2 SSDs come in different lengths and widths, denoted by numbers such as 2242, 2260, or 2280. The first two digits represent the width in millimetres, while the last two digits represent the length. For example, an M.2 2280 SSD is 22mm wide and 80mm long. Below is the full available list:
M.2 Size Length (mm)
22110 110
2280 80
2260 60
2242 42
2230 30
For your information, 2280 is the most common M.2 NVMe SSD found on desktop and laptop.
What are SATA SSDs?
SATA, which stands for Serial ATA, is a popular interface used for connecting storage devices to a computer. SATA SSDs are the most common type of SSD and are widely compatible with all older motherboards. They offer good performance and are relatively affordable.
SATA SSDs can be in the form of a 2.5-inch drive or an M.2 drive. M.2 SATA SSDs use the SATA interface and can be easily installed in M.2 slots on compatible motherboards.
What are PCIe SSDs?
PCIe, which stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect Express, is a high-speed interface commonly used for connecting graphics cards, network cards, and storage devices. PCIe SSDs offer even faster performance compared to SATA SSDs.
PCIe SSDs can also come in the form of a 2.5-inch drive or an M.2 drive. M.2 PCIe SSDs use the PCIe interface and provide faster data transfer speeds. They are typically more expensive than SATA SSDs but offer superior performance for tasks that require high-speed storage.
What are NVMe SSDs?
NVMe, which stands for Non-Volatile Memory Express, is a protocol designed specifically for SSDs. NVMe SSDs take advantage of the PCIe interface to deliver even faster speeds and lower latency compared to SATA and PCIe SSDs.
Similar to PCIe SSDs, NVMe SSDs can be in the form of a 2.5-inch drive or an M.2 drive. M.2 NVMe SSDs are the most common type and are highly sought after for their exceptional performance. However, it’s important to note that not all M.2 slots support NVMe SSDs, and compatibility varies depending on the motherboard.
How to Identify Which M.2 SSD is Compatible with Your Motherboard?
Before purchasing an M.2 SSD, it’s crucial to ensure compatibility with your motherboard. Here are some steps to help you determine if an M.2 SSD is compatible:
1. Check your motherboard documentation: Consult the user manual or visit the manufacturer’s website to find information about M.2 slots and supported SSD types.
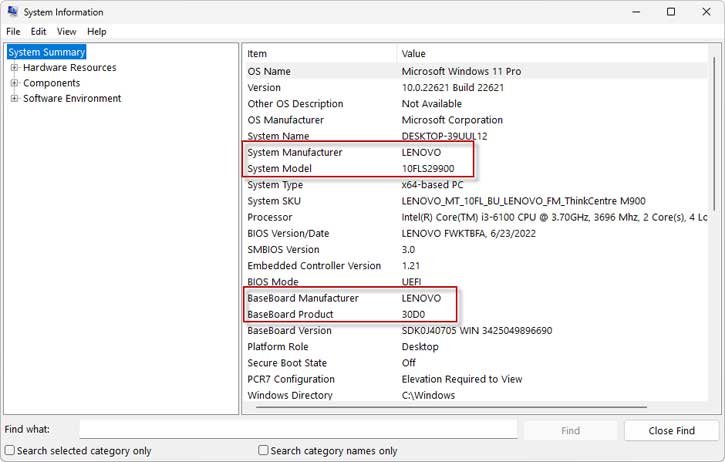
If you don’t know the exact name of your PC’s motherboard, simply go to your Start menu and type system information. Open the System information and in System Summery page, check for baseboard manufacturer name and baseboard product. Use these two information to search the web for details.
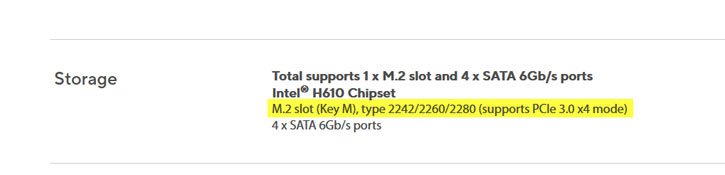
2. Identify the keying of the M.2 slot: M.2 SSDs have different key notches, denoted by letters such as B, M, or B+M (see above screenshot). The keying determines the type of SSD that can be inserted into the slot. Refer to the motherboard documentation to determine the supported key type.
3. Consider the length and width: Determine the available space in your computer case and check if the M.2 SSD you are considering will fit properly. Look for the M.2 slot length specification in the motherboard documentation.
4. Check for compatibility with SATA or NVMe: Some M.2 slots support both SATA and NVMe SSDs, while others may only support one type. Make sure to verify the supported interface before purchasing an M.2 SSD.
By following these steps and referring to your motherboard documentation, you can ensure that the M.2 SSD you choose is compatible with your motherboard.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between M.2, SATA, PCIe, and NVMe SSDs is essential when choosing the right storage solution for your computer. M.2 SSDs offer compactness and convenience, while SATA, PCIe, and NVMe SSDs provide varying levels of performance. By checking the compatibility of an M.2 SSD with your motherboard, you can make an informed decision and enjoy the benefits of faster and more reliable storage.
